![]() Trace elements (Mineral) : LA-ICP-MS
Trace elements (Mineral) : LA-ICP-MS
Concentration analyses for trace elements of silicates were performed using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS) set up at the Department of Geosciences, National Taiwan University. An Agilent 7500s quadrupole ICP-MS and a New Wave UP213 laser ablation system were combined for the LA-ICPMS analysis. The laser ablation was performed with a helium carrier gas to reduce the deposition of ablated material onto the sample surface, which can significantly improve transport efficiency and thus increase the signal intensities. The routine ablation conditions include spot size of 40 mm, laser repetition rate of 4 Hz and laser energy density of 10 J/cm2. The NIST SRM 610 was used to optimize the operation condition throughout LA-ICPMS experiment, during which time-resolved analysis (TRA) and peak hopping scanning mode (1point per peak and 30 ms of dwell time per isotope) were applied for data acquisition. Data acquisition time for each spot was about 130 s, i.e. 60 s gas blank followed with 70 s ablation. Data calibration was performed using NIST SRM 610 with internal standardization by Ca. Concentrations of NIST SRM 610 used for the external calibration are from Norman et al. (1996). Coupled USGS glass standards, BCR-2G and BHVO-2, were used as secondary standards for data quality control. All isotopic concentrations were calculated using the GLITTER 4.0 (GEMOC) software.
Analytical results of the secondary standards BCR-2G and BHVO-2 are listed with precision as 1 s relative standard deviation (% RSD) in Fig. 1a. The precision for 37 major and trace elements is generally better than 10%, except Sb (15.8%) in BCR-2G and Sb (23.1%), Cs (20.5%) and W (15.2%) in BHVO-2. Literature reference values of BCR-2G and BHVO-2 are also listed in Table 1 and Table 2 for comparison, with their relative deviations being plotted in Figs. 1b and 1c.
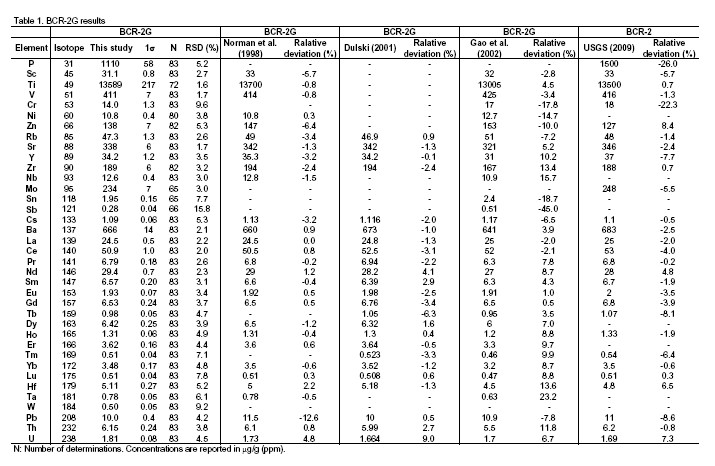

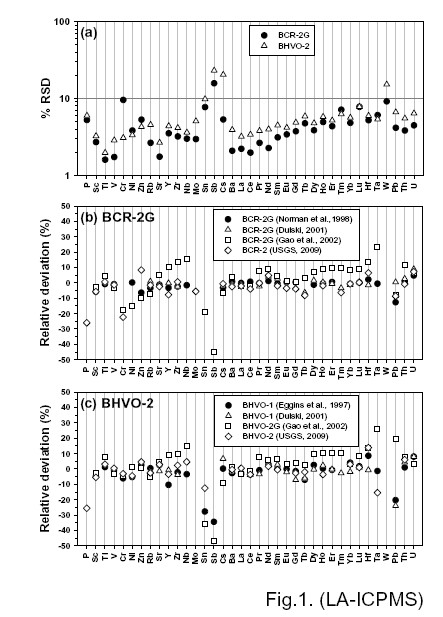
Fig.1. (a) Relative standard deviation (RSD) for elements analyzed in BCR-2G and BHVO-2. Relative deviation of average concentrations in (b) BCR-2G and (c) BHVO-2 obtained in this study from reference values.